ABOUT
project
This project aims at providing new efficient decision making tools for helping agricultural development as well as biodiversity protection in Peru. More precisely it aims at developing a new platform for helping to acquire new data, to share data, to extract knowledge, and to share useful information and knowledge among different actors that are involved in agriculture or biodiversity domains in Peru.
1. Introduction
Helping agricultural development, preserving the biodiversity are, for instance, goals that have been recognized as very important for several years. Today with the development of new technologies in ICT new opportunities are offered. Actually many information are available today: farmer or expert experiences, information about the meteorological trends, economical information, scientific publications, satellite images, etc. in order to analyze trends, formal or informal exchanged information, etc. This is typically the goal addressed in the new Big Data era. Informally Big Data is defined as: “is an all-encompassing term for any collection of data sets so large and complex that it becomes difficult to process using on-hand data management tools or traditional data processing applications » (Wikipedia).
The BIrthDAY (BIg Data for Agriculture and biodiversitY) project aims at providing a Collaborative Decision Making Platform. Based on the experiments of Peru on the two following topics: Coffee Rust and Biodiversity we will first focus on these applications. Actually, the platform is expected to be as generic as possible (this is specifically why the general architecture is defined by used modules) in order to be applied on different domains where sharing information, additional information, data mining and visualization techniques are necessary. To name a few we can have: impact of the traffic on the population, unsafe cities, more general diseases for plants or animals, quality of water, etc. In the following we will illustrate the main concepts through the Coffee Rust example. Basically, the main functionalities that will be provided by this platform are the followings:
- An easy way for the farmer to query the system in order to know the gravity of the disease. Through the platform the farmer can automatically download pictures of the leaves and give information about the treatment.
- A real technology watch for the expert in order to automatically know the scientific publications relevant with the studied disease. Furthermore by having information provided by the farmers, the expert will be provided by visual tools in order to better evaluate propagation of disease, trends, or any historical evolution. Furthermore as the platform is connected to open data information from meteorological web services as well as regional newspapers he will be informed about all the contexts of the diseases.
2.Towards a Collaborative Decision Making Platform
First efficient data mining techniques will be applied in order to better classify the
different kinds of diseases. These techniques will highlight the most representative
characteristics of each disease and with the help of the expert different treatments
could be proposed according to the severity of the disease.
In order to better evaluate the context of the disease, an open data access to
meteorological data will be performed. This module will automatically add informative
context in order to propose the most efficient treatment. Furthermore for the expert,
this valuable information will be very useful to better evaluate the evolution of a
disease.
By incorporating regional newspaper in the process, the expert will also be provided
with other contextual information that could be helpful for giving advices to the
farmers. Textual information will also be provided through an automatic extraction of
the most relevant scientific publications. This tool will be very helpful for updating on
real time the knowledge of the expert. These two modules will use new text mining
approaches that will focus on location in documents and on an efficient analysis of
the contents of scientific documents.
All the information that will be provided by farmers will be stored in order to apply
new spatio-temporal algorithms that will be take into account contextual information.
Based on the historical data, this module will thus be used in order to predict the
evolution of a disease in different regions and then will help both experts and farmers
to anticipate some treatments.
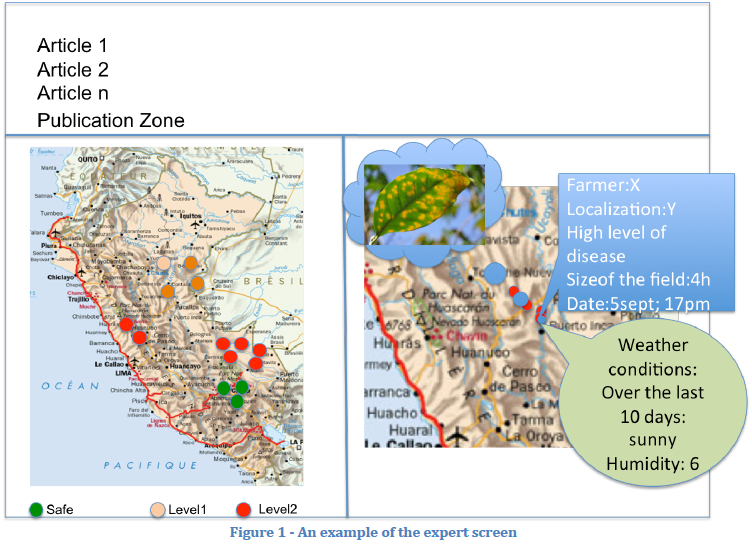
Figure 1 Figure1-‐ An example of the expert screen illustrates one screenshot of the
interface that will be provided to the expert. At the top, a specific area will be
dedicated for scientific publications. On left there is a global view of all the farmer
pictures. This view will also provide information about severity of disease. On right
the expert can zoom on the map in order to focus on a more specific region and also
get all the contextual information that are embedded in the system.
3. A Pluridisciplinary and Complementary Consortium
In order to achieve this project a complementary consortium has been defined. It is composed of teams having a strong experiment on Big Data, Pattern Recognition, Data Mining and Semantic Web. All these domains form the core of the platform. Furthermore members of the Pontificia Universidad Católica del Perú and from the University of Montpellier have already worked together and obtained several publications in some leader journals. Peruvian teams also have a strong background on Big Data and are the organizers of the first and second International Symposium on the Management of Big Data (Cusco, September 2014) (http://www.lirmm.fr/simbig2014) (Cusco, September 2015) (http://simbig.org/SIMBig2015/)